CreateML 使用以及在 iOS 中应用介绍
aPaaS Growth 团队专注在用户可感知的、宏观的 aPaaS 应用的搭建流程,及租户、应用治理等产品路径,致力于打造 aPaaS 平台流畅的 “应用交付” 流程和体验,完善应用构建相关的生态,加强应用搭建的便捷性和可靠性,提升应用的整体性能,从而助力 aPaaS 的用户增长,与基础团队一起推进 aPaaS 在企业内外部的落地与提效。
在低代码/无代码领域,例如 MS Power Platform,AWS 的 Amplify 都有类似于 AI Builder 的产品,这些产品主要让用户很低门槛训练自己的深度学习模型,CreateML 是苹果生态下的产品,工具上伴随 XCode 下发,安装了 XCode 的同学也可以打开来体验一下(得自己准备数据集)。
什么是 CreateML
Create ML 是苹果于2018年 WWDC 推出的生成机器学习模型的工具。它可以接收用户给定的数据,生成 iOS 开发中需要的机器学习模型(Core ML 模型)。
iOS 开发中,机器学习模型的获取主要有以下几种:
- 从苹果的官方主页[1]下载现成的模型。2017年有4个现成的模型,2018年有6个,2019年增加到了9个(8个图片、1个文字),今年进展到了 13,数量有限,进步速度缓慢,但是这些模型都是比较实用的,能在手机上在用户体验允许的情况下能够跑起来的。
- 用第三方的机器学习框架生成模型,再用 Core ML Tools 转成 Core ML 模型。2017年苹果宣布支持的框架有6个,包括 Caffee、Keras。2018年宣布支持的第三方框架增加到了11个,包括了最知名的 TensorFlow、IBM Watson、MXNet。至此 Core ML 已经完全支持市面上所有主流的框架。
- 用 Create ML 直接训练数据生成模型。2018年推出的初代 Create ML有三个特性:使用 Swift 编程进行操作、用 Playground 训练和生成模型、在 Mac OS 上完成所有工作。
今年的 Create ML 在易用性上更进一步:无需编程即可完成操作、独立成单独的 Mac OS App、支持更多的数据类型和使用场景。
CreateML 模型列表

1、Image Classification:图片分类
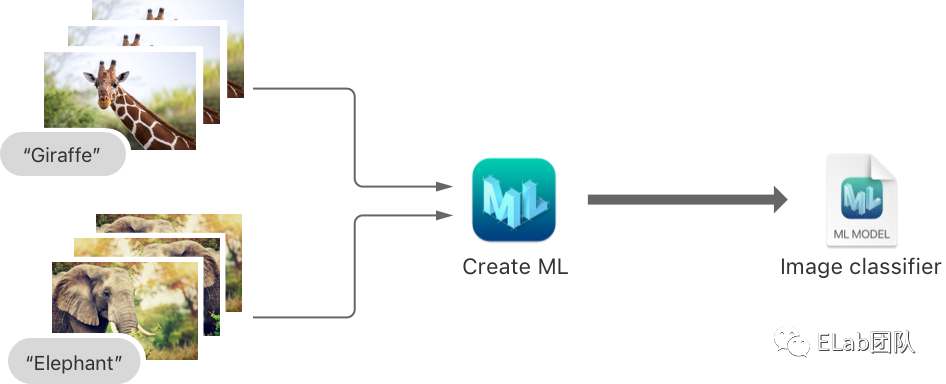
2、Object Detection:

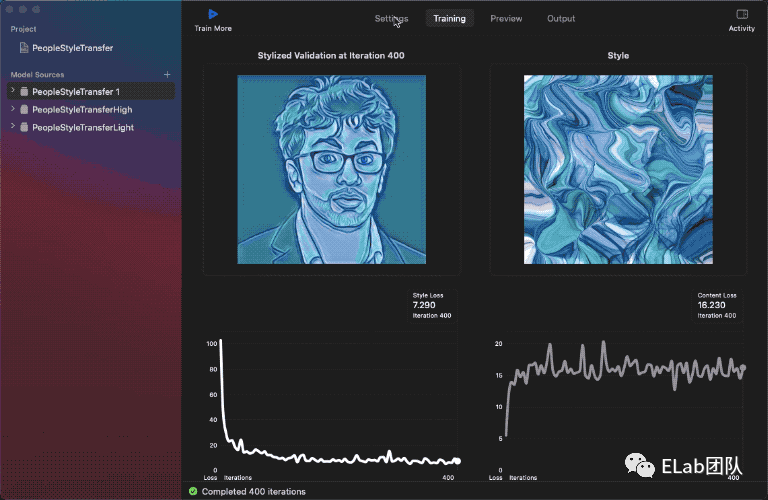
3、Style Transfer
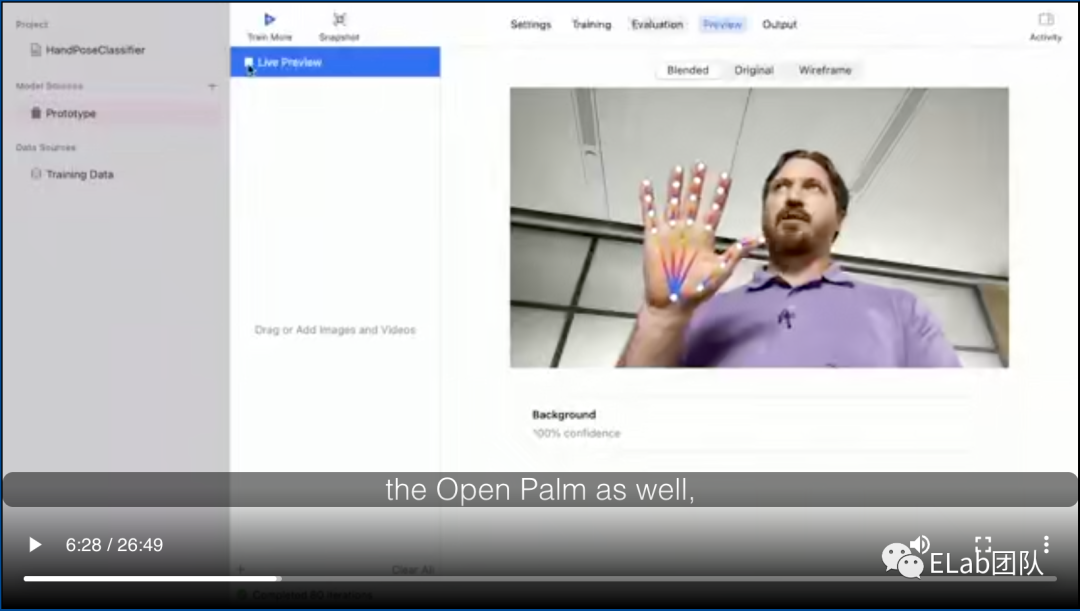
4、Hand Pose & Hand Action
5、Action Classification
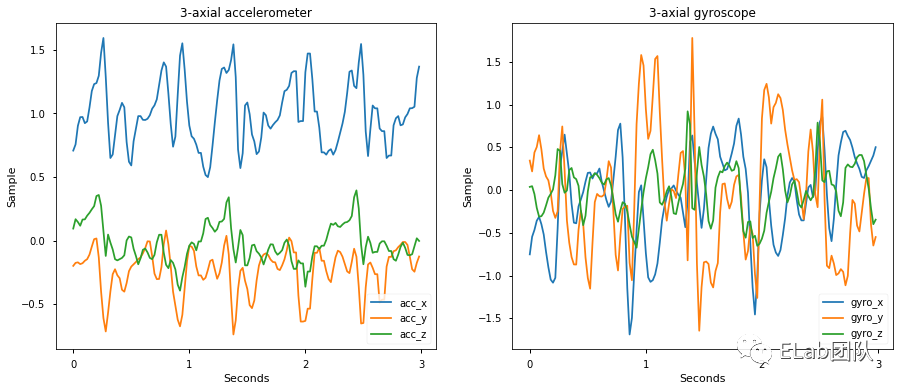
6、Activity Classification

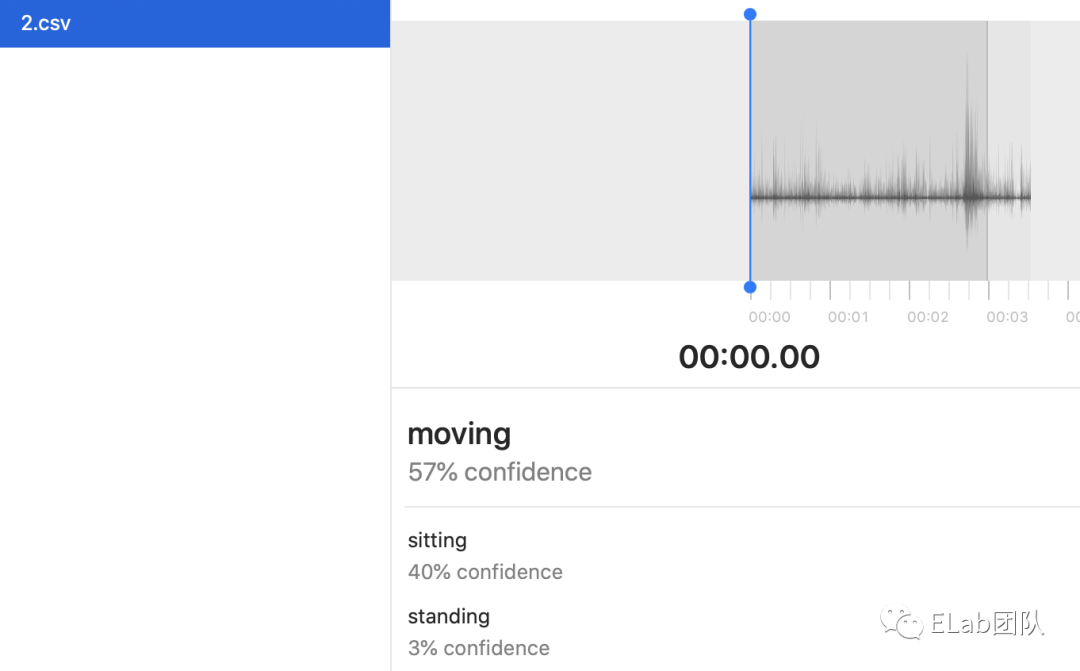
7、Sound Classification
想象一下「Hey Siri」实现
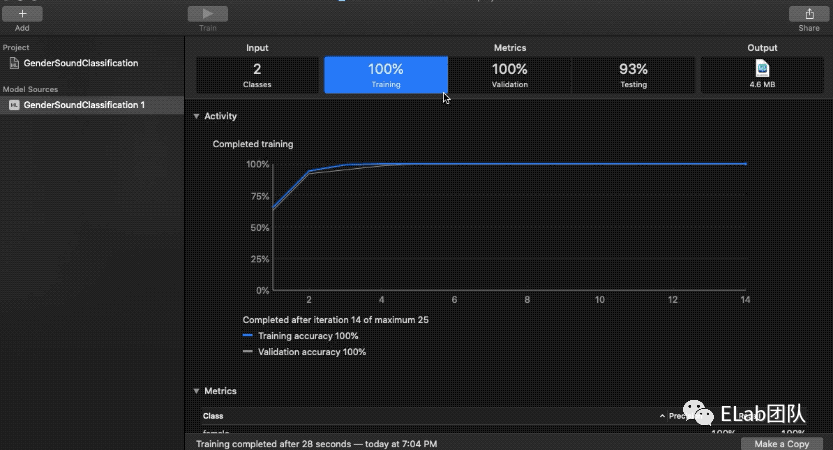
8、Text Classification

9、Word Tagging
10、Tabular Classification & Regression

通过若干个维度,预测另外一个维度,例如通过性别、年龄、城市等推断你的收入级别。
11、Recommendation
例如你买了啤酒,推荐你买花生。历史上的也有一些不是基于深度学习的算法,例如 Apriori 等。
CreateML 模型尝鲜

训练一个目标检测的 CreateML 模型
数据准备
有些同学可能认为觉得训练深度模型的难点在于找到适当的算法/模型、在足够强的机器下训练足够多的迭代次数。但是事实上,对于深度模型来说,最最最关键的是具有足够多的、精确的数据源,这也是 AI 行业容易形成头部效应最主要原因。假设你在做一个 AI 相关的应用,最主要需要关注的是如何拥有足够多的、精确的数据源。
下面我就与上面「尝鲜」的模型为例,讲述如何训练类似模型的。
数据格式
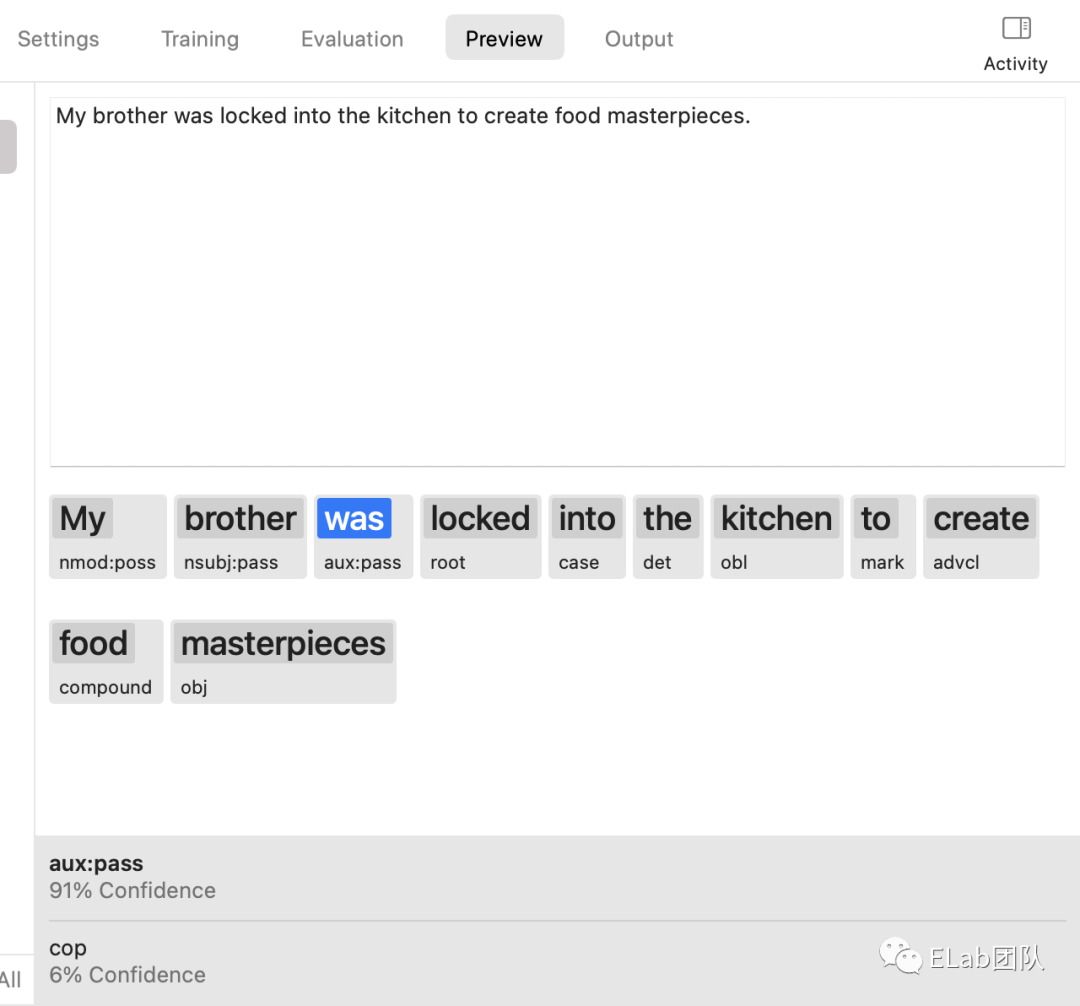
CreateML 目标检测的数据格式如下图:
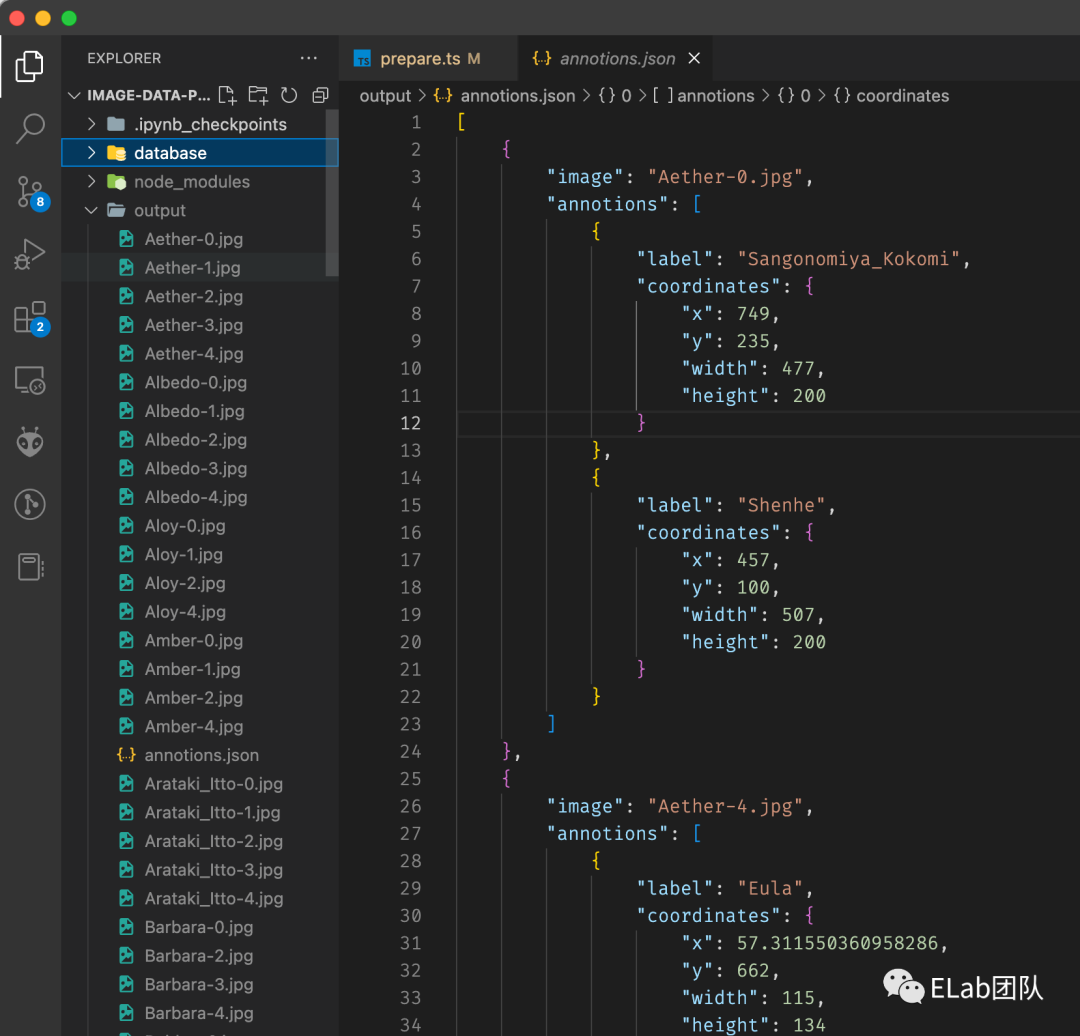
首先会有一个叫 annotions.json 的文件,这个文件会标注每个文件里有多少个目标,以及目标的 Bounding Box 的坐标是什么。

例如上图对应的 Bounding Box 如下:

准备足够多的数据
第一个问题是,什么才叫足够多的数据,我们可以看一些 Dataset 来参考一下:
Standford Cars Dataset: 934MB. The Cars dataset contains 16,185 images of 196 classes of cars. The data is split into 8,144 training images and 8,041 testing images。
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/kmader/food41: Labeled food images in 101 categories from apple pies to waffles, 6GB
在上面这个例子里,原神的角色有大概 40 多个,所以我们需要准备大概百来 MB 的数据来训练作为起来,当精确度不高的时候,再增加样本的数量来增加精度。问题是我们去哪里找那么多数据呢?所以我想到的一个方法是通过脚本来合成,因为我们的问题只是定位提取图片中的角色「证件照」,我用大概 40 来角色的证件照,写了如下的脚本(colipot helped a alot ...)来生成大概 500MB 的测试训练集:
// import sharp from "sharp";
import { createCanvas, Image } from "@napi-rs/canvas";
import { promises } from "fs";
import fs from "fs";
import path from "path";
import Sharp from "sharp";
const IMAGE_GENERATED_COUNT_PER_CLASS = 5;
const MAX_NUMBER_OF_CLASSES_IN_SINGLE_IMAGE = 10;
const CANVAS_WIDTH = 1024;
const CANVAS_HEIGHT = 800;
const CONCURRENT_PROMISE_SIZE = 50;
const CanvasSize = [CANVAS_WIDTH, CANVAS_HEIGHT];
function isNotOverlap(x1: number, y1: number, width1: number, height1: number, x2: number, y2: number, width2: number, height2: number) {
return x1 >= x2 + width2 || x1 + width1 <= x2 || y1 >= y2 + height2 || y1 + height1 <= y2;
}
const randomColorList: Record<string, string> = {
"white": "rgb(255, 255, 255)",
"black": "rgb(0, 0, 0)",
"red": "rgb(255, 0, 0)",
"green": "rgb(0, 255, 0)",
"blue": "rgb(0, 0, 255)",
"yellow": "rgb(255, 255, 0)",
"cyan": "rgb(0, 255, 255)",
"magenta": "rgb(255, 0, 255)",
"gray": "rgb(128, 128, 128)",
"grey": "rgb(128, 128, 128)",
"maroon": "rgb(128, 0, 0)",
"olive": "rgb(128, 128, 0)",
"purple": "rgb(128, 0, 128)",
"teal": "rgb(0, 128, 128)",
"navy": "rgb(0, 0, 128)",
"orange": "rgb(255, 165, 0)",
"aliceblue": "rgb(240, 248, 255)",
"antiquewhite": "rgb(250, 235, 215)",
"aquamarine": "rgb(127, 255, 212)",
"azure": "rgb(240, 255, 255)",
"beige": "rgb(245, 245, 220)",
"bisque": "rgb(255, 228, 196)",
"blanchedalmond": "rgb(255, 235, 205)",
"blueviolet": "rgb(138, 43, 226)",
"brown": "rgb(165, 42, 42)",
"burlywood": "rgb(222, 184, 135)",
"cadetblue": "rgb(95, 158, 160)",
"chartreuse": "rgb(127, 255, 0)",
"chocolate": "rgb(210, 105, 30)",
"coral": "rgb(255, 127, 80)",
"cornflowerblue": "rgb(100, 149, 237)",
"cornsilk": "rgb(255, 248, 220)",
"crimson": "rgb(220, 20, 60)",
"darkblue": "rgb(0, 0, 139)",
"darkcyan": "rgb(0, 139, 139)",
"darkgoldenrod": "rgb(184, 134, 11)",
"darkgray": "rgb(169, 169, 169)",
"darkgreen": "rgb(0, 100, 0)",
"darkgrey": "rgb(169, 169, 169)",
"darkkhaki": "rgb(189, 183, 107)",
"darkmagenta": "rgb(139, 0, 139)",
"darkolivegreen": "rgb(85, 107, 47)",
"darkorange": "rgb(255, 140, 0)",
"darkorchid": "rgb(153, 50, 204)",
"darkred": "rgb(139, 0, 0)"
}
function generateColor(index: number = -1) {
if (index < 0 || index > Object.keys(randomColorList).length) {
// return random color from list
let keys = Object.keys(randomColorList);
let randomKey = keys[Math.floor(Math.random() * keys.length)];
return randomColorList[randomKey];
} else {
// return color by index
let keys = Object.keys(randomColorList);
return randomColorList[keys[index]];
}
}
function randomPlaceImagesInCanvas(canvasWidth: number, canvasHeight: number, images: number[][], overlapping: boolean = true) {
let placedImages: number[][] = [];
for (let image of images) {
let [width, height] = image;
let [x, y] = [Math.floor(Math.random() * (canvasWidth - width)), Math.floor(Math.random() * (canvasHeight - height))];
let placed = false;
for (let placedImage of placedImages) {
let [placedImageX, placedImageY, placedImageWidth, placedImageHeight] = placedImage;
if (overlapping || isNotOverlap(x, y, width, height, placedImageX, placedImageY, placedImageWidth, placedImageHeight)) {
placed = true;
}
}
placedImages.push([x, y, placed ? 1 : 0]);
}
return placedImages;
}
function getSizeBasedOnRatio(width: number, height: number, ratio: number) {
return [width * ratio, height];
}
function cartesianProductOfArray(...arrays: any[][]) {
return arrays.reduce((a, b) => a.flatMap((d: any) => b.map((e: any) => [d, e].flat())));
}
function rotateRectangleAndGetSize(width: number, height: number, angle: number) {
let radians = angle * Math.PI / 180;
let cos = Math.abs(Math.cos(radians));
let sin = Math.abs(Math.sin(radians));
let newWidth = Math.ceil(width * cos + height * sin);
let newHeight = Math.ceil(height * cos + width * sin);
return [newWidth, newHeight];
}
function concurrentlyExecutePromisesWithSize(promises: Promise<any>[], size: number): Promise<void> {
let promisesToExecute = promises.slice(0, size);
let promisesToWait = promises.slice(size);
return Promise.all(promisesToExecute).then(() => {
if (promisesToWait.length > 0) {
return concurrentlyExecutePromisesWithSize(promisesToWait, size);
}
});
}
function generateRandomRgbColor() {
return [Math.floor(Math.random() * 256), Math.floor(Math.random() * 256), Math.floor(Math.random() * 256)];
}
function getSizeOfImage(image: Image) {
return [image.width, image.height];
}
async function makeSureFolderExists(path: string) {
if (!fs.existsSync(path)) {
await promises.mkdir(path, { recursive: true });
}
}
// non repeatly select elements from array
async function randomSelectFromArray<T>(array: T[], count: number) {
let copied = array.slice();
let selected: T[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
let index = Math.floor(Math.random() * copied.length);
selected.push(copied[index]);
copied.splice(index, 1);
}
return selected;
}
function getFileNameFromPathWithoutPrefix(path: string) {
return path.split("/").pop()!.split(".")[0];
}
type Annotion = {
"image": string,
"annotions": {
"label": string,
"coordinates": {
"x": number,
"y": number,
"width": number,
"height": number
}
}[]
}
async function generateCreateMLFormatOutput(folderPath: string, outputDir: string, imageCountPerFile: number = IMAGE_GENERATED_COUNT_PER_CLASS) {
if (!fs.existsSync(path.join(folderPath, "real"))) {
throw new Error("real folder does not exist");
}
let realFiles = fs.readdirSync(path.join(folderPath, "real")).map((file) => path.join(folderPath, "real", file));
let confusionFiles: string[] = [];
if (fs.existsSync(path.join(folderPath, "confusion"))) {
confusionFiles = fs.readdirSync(path.join(folderPath, "confusion")).map((file) => path.join(folderPath, "confusion", file));
}
// getting files in folder
let tasks: Promise<void>[] = [];
let annotions: Annotion[] = [];
for (let filePath of realFiles) {
let className = getFileNameFromPathWithoutPrefix(filePath);
for (let i = 0; i < imageCountPerFile; i++) {
let annotion: Annotion = {
"image": `${className}-${i}.jpg`,
"annotions": []
};
async function __task(i: number) {
let randomCount = Math.random() * MAX_NUMBER_OF_CLASSES_IN_SINGLE_IMAGE;
randomCount = randomCount > realFiles.length + confusionFiles.length ? realFiles.length + confusionFiles.length : randomCount;
let selectedFiles = await randomSelectFromArray(realFiles.concat(confusionFiles), randomCount);
if (selectedFiles.includes(filePath)) {
// move filePath to the first
selectedFiles.splice(selectedFiles.indexOf(filePath), 1);
selectedFiles.unshift(filePath);
} else {
selectedFiles.unshift(filePath);
}
console.log(`processing ${filePath} ${i}, selected ${selectedFiles.length} files`);
let images = await Promise.all(selectedFiles.map(async (filePath) => {
let file = await promises.readFile(filePath);
let image = new Image();
image.src = file;
return image;
}));
console.log(`processing: ${filePath}, loaded images, start to place images in canvas`);
let imageSizes = images.map(getSizeOfImage).map( x => {
let averageX = CanvasSize[0] / (images.length + 1);
let averageY = CanvasSize[1] / (images.length + 1);
return [x[0] > averageX ? averageX : x[0], x[1] > averageY ? averageY : x[1]];
});
let placedPoints = randomPlaceImagesInCanvas(CANVAS_WIDTH, CANVAS_HEIGHT, imageSizes, false);
console.log(`processing: ${filePath}, placed images in canvas, start to draw images`);
let angle = 0;
let color = generateColor(i);
let [canvasWidth, canvasHeight] = CanvasSize;
const canvas = createCanvas(canvasWidth, canvasHeight);
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
ctx.fillStyle = color;
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, canvasWidth, canvasHeight);
for (let j = 0; j < images.length; j++) {
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
let ratio = Math.random() * 1.5 + 0.5;
let image = images[j];
let [_imageWidth, _imageHeight] = imageSizes[j];
let [imageWidth, imageHeight] = getSizeBasedOnRatio(_imageWidth, _imageHeight, ratio);
let placed = placedPoints[j][2] === 1 ? true : false;
if (!placed) {
continue;
}
let targetX = placedPoints[j][0] > imageWidth / 2 ? placedPoints[j][0] : imageWidth / 2;
let targetY = placedPoints[j][1] > imageHeight / 2 ? placedPoints[j][1] : imageHeight / 2;
let sizeAfterRotatation = rotateRectangleAndGetSize(imageWidth, imageHeight, angle);
console.log("final: ", [canvasWidth, canvasHeight], [imageWidth, imageHeight], [targetX, targetY], angle, ratio, color);
ctx.translate(targetX, targetY);
ctx.rotate(angle * Math.PI / 180);
ctx.drawImage(image, -imageWidth / 2, -imageHeight / 2, imageWidth, imageHeight);
ctx.rotate(-angle * Math.PI / 180);
ctx.translate(-targetX, -targetY);
// ctx.fillStyle = "green";
// ctx.strokeRect(targetX - sizeAfterRotatation[0] / 2, targetY - sizeAfterRotatation[1] / 2, sizeAfterRotatation[0], sizeAfterRotatation[1]);
annotion.annotions.push({
"label": getFileNameFromPathWithoutPrefix(selectedFiles[j]),
"coordinates": {
"x": targetX,
"y": targetY,
"width": sizeAfterRotatation[0],
"height": sizeAfterRotatation[1]
}
});
}
if (!annotion.annotions.length) {
return;
}
let fileName = path.join(outputDir, `${className}-${i}.jpg`);
let pngData = await canvas.encode("jpeg");
await promises.writeFile(fileName, pngData);
annotions.push(annotion);
}
tasks.push(__task(i));
}
}
await concurrentlyExecutePromisesWithSize(tasks, CONCURRENT_PROMISE_SIZE);
await promises.writeFile(path.join(outputDir, "annotions.json"), JSON.stringify(annotions, null, 4));
}
async function generateYoloFormatOutput(folderPath: string) {
const annotions = JSON.parse((await promises.readFile(path.join(folderPath, "annotions.json"))).toString("utf-8")) as Annotion[];
// generate data.yml
let classes: string[] = [];
for (let annotion of annotions) {
for (let label of annotion.annotions.map(a => a.label)) {
if (!classes.includes(label)) {
classes.push(label);
}
}
}
let dataYml = `
train: ./train/images
val: ./valid/images
test: ./test/images
nc: ${classes.length}
names: ${JSON.stringify(classes)}
`
await promises.writeFile(path.join(folderPath, "data.yml"), dataYml);
const weights = [0.85, 0.90, 0.95];
const split = ["train", "valid", "test"];
let tasks: Promise<void>[] = [];
async function __task(annotion: Annotion) {
const randomSeed = Math.random();
let index = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < weights.length; i++) {
if (randomSeed < weights[i]) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
let splitFolderName = split[index];
await makeSureFolderExists(path.join(folderPath, splitFolderName));
await makeSureFolderExists(path.join(folderPath, splitFolderName, "images"));
await makeSureFolderExists(path.join(folderPath, splitFolderName, "labels"));
// get info of image
let image = await Sharp(path.join(folderPath, annotion.image)).metadata();
// generate label files
let line: [number, number, number, number, number][] = []
for (let i of annotion.annotions) {
line.push([
classes.indexOf(i.label),
i.coordinates.x / image.width!,
i.coordinates.y / image.height!,
i.coordinates.width / image.width!,
i.coordinates.height / image.height!
])
}
await promises.rename(path.join(folderPath, annotion.image), path.join(folderPath, splitFolderName, "images", annotion.image));
await promises.writeFile(path.join(folderPath, splitFolderName, "labels", annotion.image.replace(".jpg", ".txt")), line.map(l => l.join(" ")).join("/n"));
}
for (let annotion of annotions) {
tasks.push(__task(annotion));
}
await concurrentlyExecutePromisesWithSize(tasks, CONCURRENT_PROMISE_SIZE);
}
(async () => {
await generateCreateMLFormatOutput("./database", "./output");
// await generateYoloFormatOutput("./output");
})();
这个脚本的思路大概是将这 40 多张图片随意揉成各种可能的形状,然后选取若干张把它撒在画布上,画布的背景也是随机的,用来模拟足够多的场景。
顺带一说,上面 500MB 这个量级并不是一下子就定好的,而是不断试验,为了更高的准确度一步一步地提高量级。
模型训练
下一步就比较简单了,在 CreateML 上选取你的数据集,然后就可以训练了:


可以看到 CreateML 的 Object Detection 其实是基于 Yolo V2 的,最先进的 Yolo 版本应该是 Yolo V7,但是生态最健全的应该还是 Yolo V5。
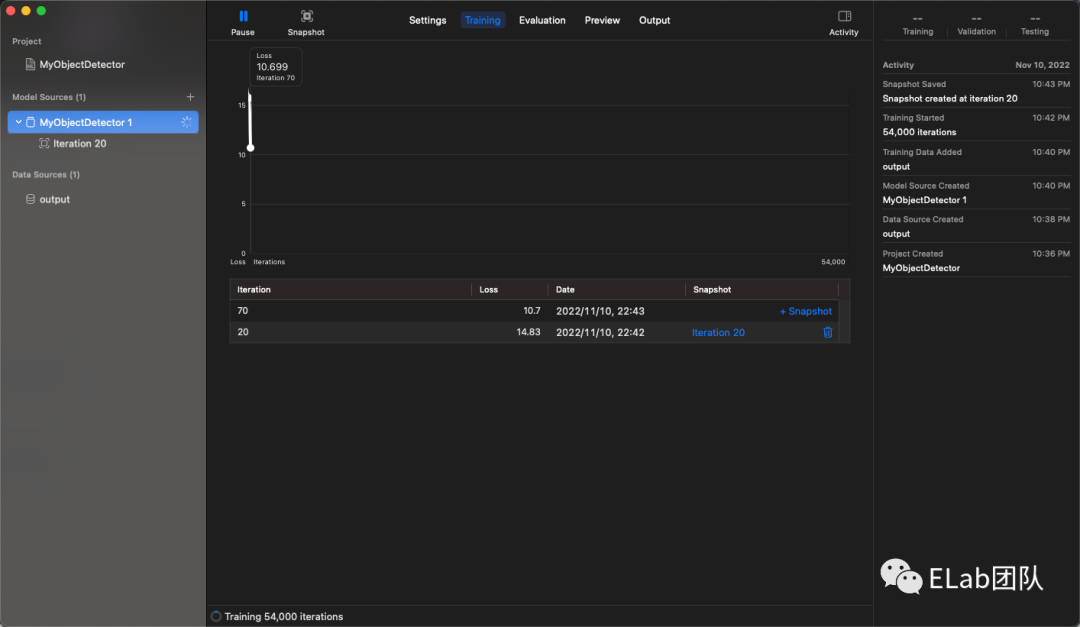
在我的 M1 Pro 机器上大概需要训练 10h+,在 Intel 的笔记本上训练时间会更长。整个过程有点像「炼蛊」了,从 500 多 MB 的文件算出一个 80MB 的文件。
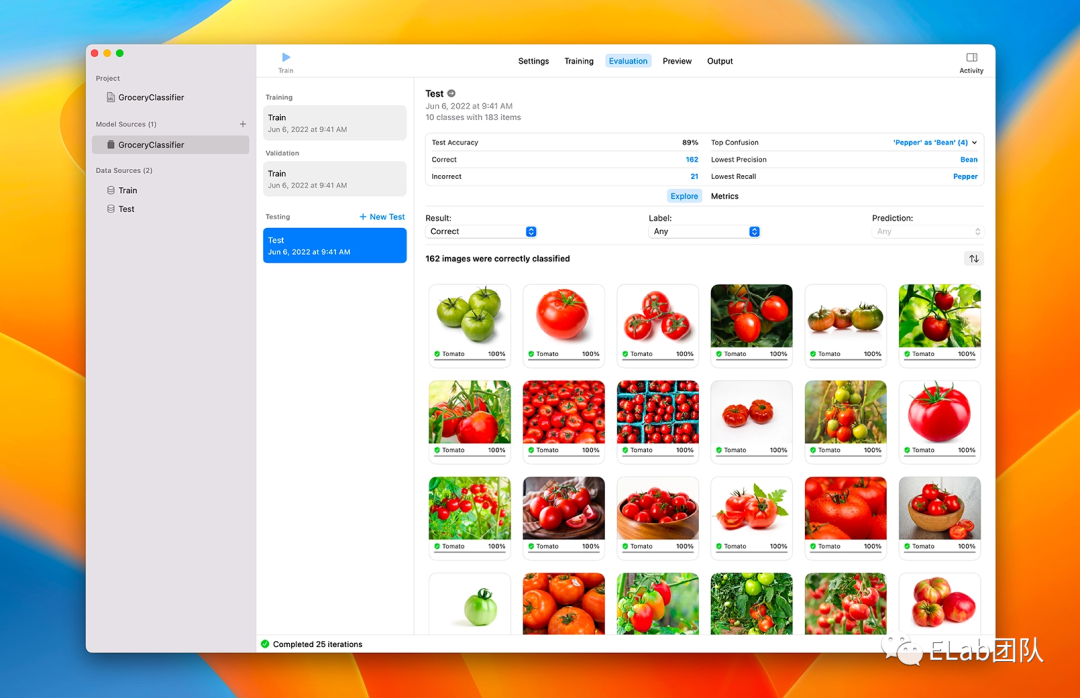
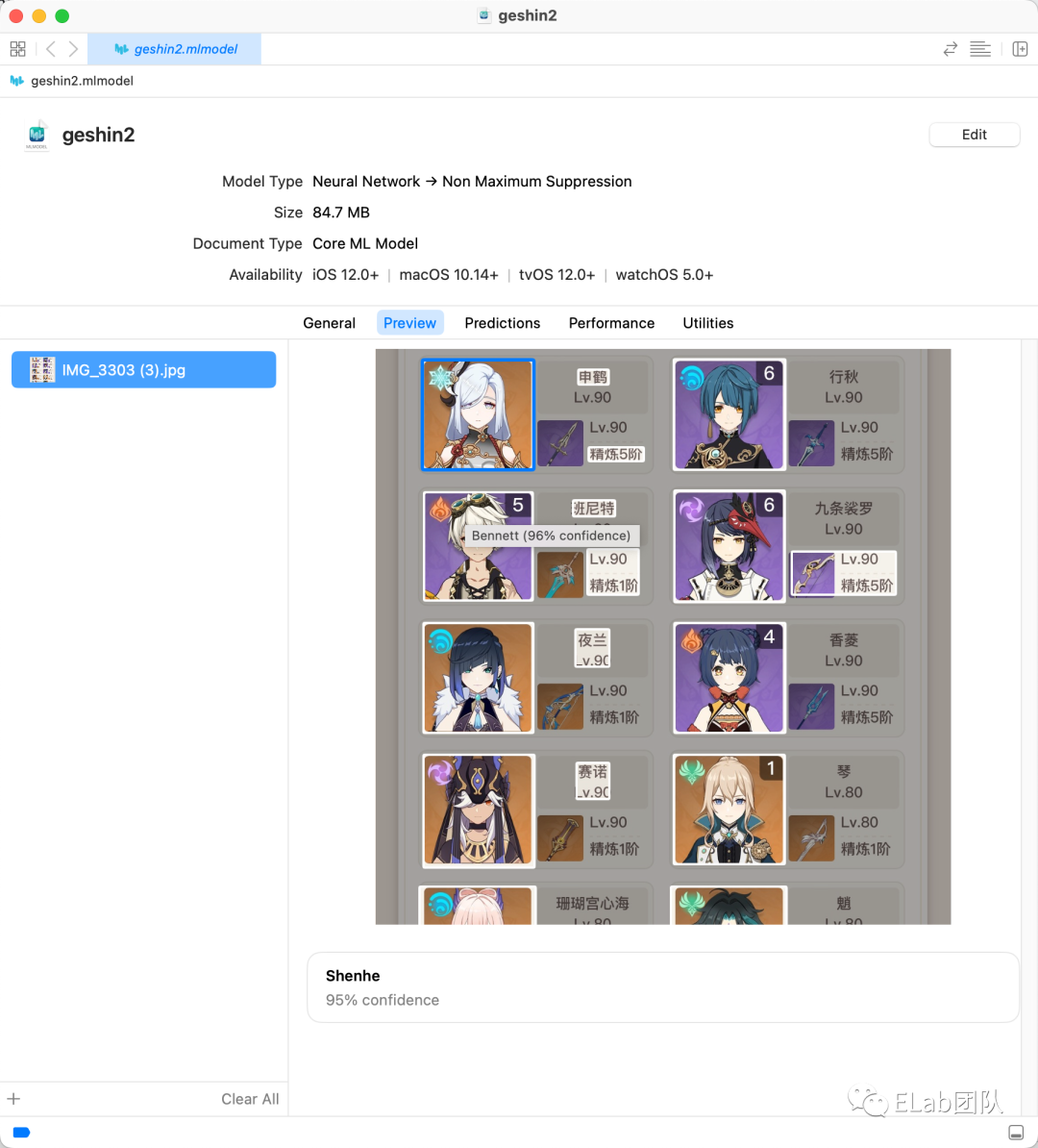
模型测试
训练完之后,你可以得到上面「尝鲜」中得到模型文件,大概它拖动任意文件进去,就可以测试模型的效果了:
- 01-11全球最受赞誉公司揭晓:苹果连续九年第一
- 12-09罗伯特·莫里斯:让黑客真正变黑
- 12-09谁闯入了中国网络?揭秘美国绝密黑客小组TA
- 12-09警示:iOS6 惊现“闪退”BUG
- 03-08消息称微软开发内部AI推理模型,或将成为Op
- 03-08美国法院驳回马斯克请求,未阻止OpenAI转型
- 03-08饿了么成立即时配送算法专家委员会 持续全局
- 03-08长安汽车:预计今年底长安飞行汽车将完成试
- 03-08谷歌推出虚拟试穿、AR美妆新功能




















 粤公网安备 44060402001498号
粤公网安备 44060402001498号